Genetica. 2024 Aug 31:1-4.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-024-00211-6
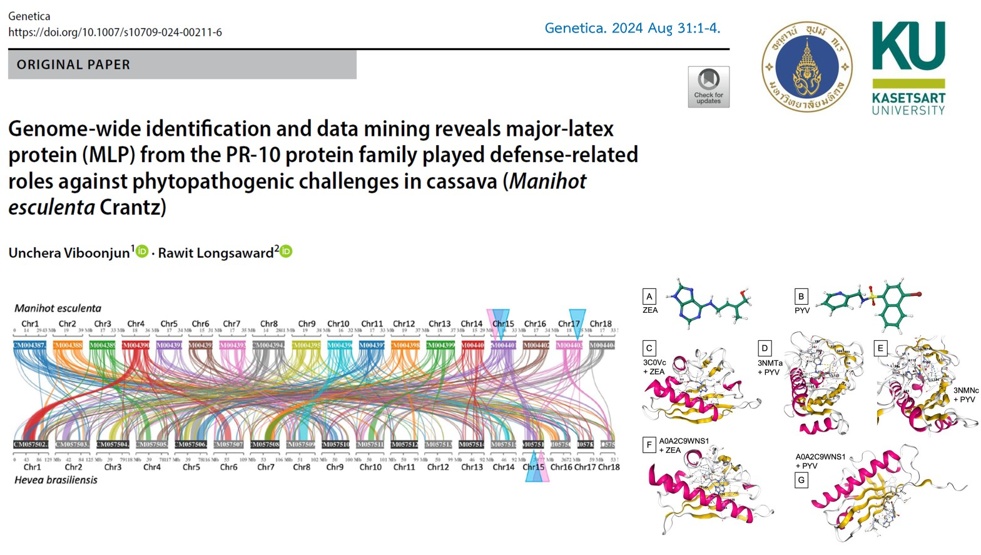
Although previously identified in some studies, the pathogenesis-related 10 (PR-10) protein has not been well studied and remains underexplored in many plant species. This research uses data mining techniques to study PR-10 proteins in cassava, a key global crop. The study focused on 53 PR-10 proteins found in cassava using in silico methods. These proteins are divided into two main groups: 34 major latex proteins (MLPs) and 13 major allergen proteins, called Pru ar 1, based on their evolutionary relationships. A genome comparison with the rubber tree suggests a possible evolutionary link between PR-10 genes in these two Euphorbiaceae species, particularly on chromosome 15. Notably, MLP423 and other MLP proteins were found in several published cassava transcriptome datasets, showing responses to pathogens like anthracnose fungus, viruses, and bacterial blight. Ligand prediction and molecular docking of three MLP423 proteins showed possible interactions with cytokinin and abscisic acid hormones. Their expression levels and predicted binding strengths are discussed, emphasizing their role in cassava’s defense against major diseases.
งานวิจัยนี้วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลของโปรตีน PR-10 ในมันสำปะหลังซึ่งเป็นพืชเศรษฐกิจสำคัญของไทย โดยทำการระบุชนิดโปรตีนในกลุ่ม PR-10 ด้วยวิธีการทางชีวสารสนเทศ พบโปรตีน PR-10 ทั้งหมด 53 ชนิดที่สามารถแบ่งออกเป็นสองกลุ่ม ได้แก่ โปรตีน major latex proteins (MLPs) จำนวน 34 ชนิด และโปรตีนที่ก่อให้เกิดอาการแพ้ในกลุ่ม Pru ar 1 จำนวน 13 ชนิด และยังพบอีกว่ายีนของโปรตีนดังกล่าวมีความสอดคล้องกับยีนของโปรตีนเดียวกันบนจีโนมของยางพารา แสดงให้เห็นถึงความเป็นไปได้ในความสัมพันธ์ทางวิวัฒนาการของยีน PR-10 ระหว่างพืชในสกุล Euphorbiaceae ทั้งสองชนิด โดยเฉพาะบนโครโมโซมที่ 15 นอกจากนี้ในฐานข้อมูลทรานสคริปโตมของมันสำปะหลังแสดงให้เห็นว่า โปรตีน MLP423 และโปรตีน MLP บางชนิด มีการตอบสนองต่อเชื้อก่อโรคพืช รวมถึงเชื้อราแอนแทรคโนส ไวรัส และแบคทีเรีย การทำนายการจับตัวของโมเลกุลโปรตีน MLP423 กับลิแกนด์ เผยให้เห็นความเป็นไปได้ในการมีปฏิสัมพันธ์กับฮอร์โมนพืช ไซโตไคนิน และกรดแอบไซซิก การแสดงออกของโปรตีนกลุ่มนี้และความสามารถในการจับกับฮอร์โมนพืชดังกล่าว แสดงถึงบทบาทของ PR-10 ในตอบสนองและป้องกันการเกิดโรคสำคัญในมันสำปะหลัง